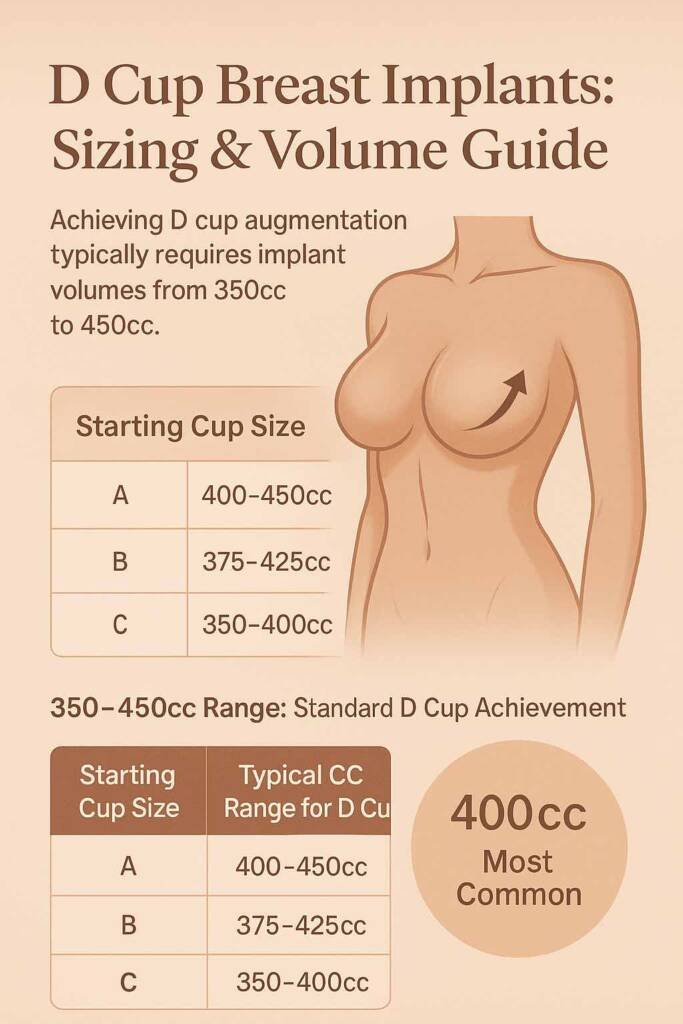
D cup breast implants represent one of the most sought-after enhancements in cosmetic surgery. They offer women a significant yet proportionate transformation that balances dramatic results with natural aesthetics. This comprehensive enhancement typically requires implant volumes between 350cc and 450cc, with 400cc representing the single most frequently selected volume across all augmentation procedures.
The decision to pursue D cup augmentation involves careful consideration of your unique anatomy, lifestyle demands, and long-term aesthetic goals. Unlike smaller enhancements that may go unnoticed, D cup results create noticeable fullness, enhanced cleavage, and improved body proportions. These changes can dramatically boost confidence and self-image.
This guide provides everything you need to make an informed decision about D cup breast augmentation. It covers understanding the technical aspects of implant sizing to navigating the consultation process. You’ll also learn about planning for long-term maintenance.
D Cup Breast Augmentation Cup Size Options
D cup breast augmentation creates substantial volume and projection that significantly enhances your natural figure. This enhancement level produces noticeable fullness in the upper breast area, increased cleavage, and enhanced projection from the chest wall. These characteristics distinguish D cup results from more modest augmentations.
The key to successful D cup augmentation lies in understanding how implant volume translates to aesthetic outcomes. Unlike natural breast sizing, surgical augmentation focuses on creating proportional results that complement your frame. The goal is proportional enhancement rather than simply achieving a specific cup designation.
Size and Bra Cup Volume
Surgeons measure implants in cubic centimeters (cc) rather than bra cup sizes because this provides precise, standardized measurements for predictable outcomes. As a practical guideline, every 150–200cc of implant volume is commonly cited as correlating to approximately one cup size increase, though major implant manufacturers do not provide official volume-to-cup-size guidelines due to significant individual anatomical variation.
Key volume relationships include:
- 350–450cc range: Standard D cup achievement
- 400cc: Most frequently selected volume for balanced enhancement
- Base diameter: Ranges from 7.4cm to 17.2cm, fundamentally shaping breast contours
The volume requirements for achieving D cup results vary based on your starting point:
| Starting Cup Size | Typical CC Range for D Cup |
| A Cup | 400–450cc |
| B Cup | 375–425cc |
| C Cup | 350–400cc |
Understanding these progressions helps visualize potential outcomes. Patients starting from B cups typically achieve D cup results with 350–400cc implants. Those beginning with A cups often require 370–430cc for similar fullness.
Factors Influencing Volume
Several anatomical factors determine the exact volume needed to achieve your desired D cup appearance. Chest wall dimensions play a crucial role, as broader chest walls may require larger volumes to achieve equivalent projection. Patients with narrower chests often achieve D cup results with volumes at the lower end of the range.
Existing breast tissue significantly impacts final appearance and required volume. Women with little breast tissue may need additional volume to achieve the same cup size as those with more existing tissue.
Skin elasticity determines your tissue’s ability to accommodate larger volumes safely. Poor elasticity may limit size options or require additional procedures for optimal results.
Pre-Surgical Candidacy
Successful D cup augmentation requires careful evaluation of multiple factors that influence both safety and aesthetic outcomes. Your body type, lifestyle, and aesthetic goals all play crucial roles. These factors determine whether D cup implants are the right choice for your situation.
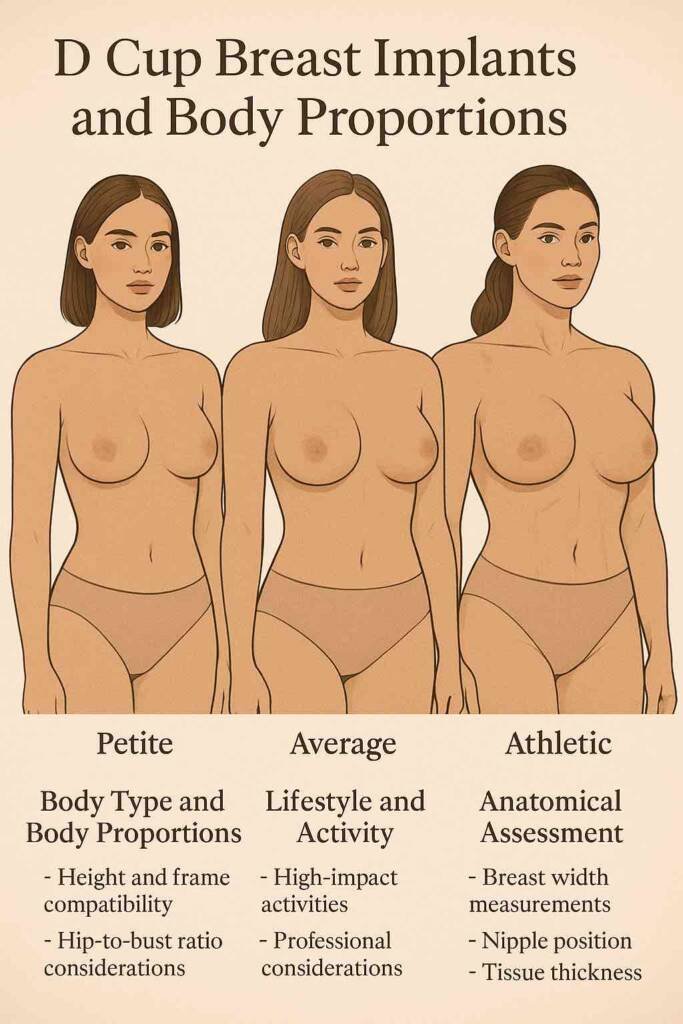
Body Type and Body Proportions
Your frame size directly impacts how D cup implants will appear and feel on your body. Women with broader shoulders and wider ribcages typically accommodate larger implants more naturally. Petite frames may find D cup volumes overwhelming their natural proportions.
Height and frame compatibility significantly affects proportional balance. Taller women often find that D cup implants complement their overall silhouette better. Shorter individuals may discover that the same implant size appears more dramatic on their frame.
Hip-to-bust ratio considerations ensure balanced proportions. Women with fuller hips often benefit from D cup implants to create an hourglass figure. Those with narrower hips might find that a smaller implant maintains better overall harmony.
Selecting implants that overwhelm a petite frame can potentially lead to chronic discomfort and postural strain. This makes proportional sizing essential for long-term physical wellbeing.
Lifestyle and Activity
Your daily activities and exercise routines significantly influence implant selection and surgical planning. Athletic individuals should carefully evaluate how D cup volumes affect exercise routines and sports participation.
High-impact activities like court sports may present physical challenges during rapid directional changes with larger volumes. Low-impact exercises such as yoga or pilates allow easier adaptation to increased breast volume.
Professional considerations include wardrobe adaptability and workplace appropriateness. Some careers may require specific aesthetic considerations that influence implant size selection.
Long-term lifestyle factors matter for sustained results. These include travel schedules, support system availability during recovery, and weight stability. Significant weight fluctuations after surgery can alter how D cup implants look and feel.
Anatomical Assessment
Comprehensive anatomical evaluation determines your candidacy for D cup augmentation and influences surgical planning. Breast width measurements determine implant base compatibility. The implant base should not extend beyond your natural breast footprint for optimal results.
Surgeons precisely measure from the outer breast edge to determine maximum implant width. This ensures selected dimensions enhance projection without creating unnaturally wide appearance.
Nipple position relative to the chest influences whether additional procedures are needed. D cup implants may require simultaneous breast lifts if significant sagging exists.
Tissue thickness provides natural coverage over implants. Adequate tissue helps mask implant edges and creates more natural-looking results with larger sizes like D cups.
Implant Type Selection for D Cup Breast Results
Three main implant categories can effectively achieve D cup results. Each offers distinct advantages and characteristics that influence both immediate outcomes and long-term satisfaction.
1. Silicone Gel Implants
Silicone gel implants remain the most popular choice for D cup augmentation due to their natural feel and movement characteristics. The cohesive silicone gel closely mimics natural breast tissue. This provides realistic appearance and movement.
These pre-filled implants maintain consistent shape over time and offer superior resistance to visible rippling. This makes them particularly well-suited for patients with minimal natural breast tissue. FDA regulations approve silicone implants for cosmetic augmentation in patients aged 22 and older.
Primary advantages include:
- Most natural feel compared to other options
- Lower risk of visible rippling
- Consistent shape maintenance
- Better suited for thin tissue coverage
Silicone implants typically cost more than alternatives and require slightly larger incisions. This is because they arrive pre-filled from the manufacturer.
2. Saline and Structured Saline Options
Saline implants contain sterile salt water and offer unique benefits for D cup augmentation. These implants are inserted empty and filled during surgery, allowing precise volume adjustments. This enables surgeons to fine-tune breast symmetry by adjusting each implant’s volume independently.
Structured saline implants represent an advancement in saline technology. They contain internal baffles that control saline movement and reduce the sloshing sensation common with traditional saline implants.
Key benefits include:
- Smaller incision requirements
- Volume adjustability during surgery
- Safe rupture characteristics (body safely absorbs saline)
- Lower initial cost
Traditional saline implants may feel less natural than silicone but provide excellent safety profiles. They work well for patients prioritizing safety and adjustability.
3. Gummy Bear (Form-Stable) Implants
Gummy bear implants contain highly cohesive silicone gel that maintains shape even when cut. They offer superior durability and shape retention. The thick gel consistency prevents migration if the shell becomes damaged.
The implant maintains its anatomical teardrop shape for natural-looking results.
Distinctive features include:
- Form-stable design prevents gel migration
- Anatomical shape mimics natural breast contour
- Lower rupture rates compared to traditional implants
- Reduced risk of capsular contracture
These implants require larger incisions due to their pre-formed shape and cannot rotate without affecting appearance. This makes precise placement critical. The cohesive gel technology represents the latest advancement in breast implant design for achieving natural D cup results.
Breast Implant Profiles and Shape Selection
The shape and profile of your D cup implants significantly impact final appearance and projection. Understanding these characteristics helps ensure your results align with your aesthetic vision.
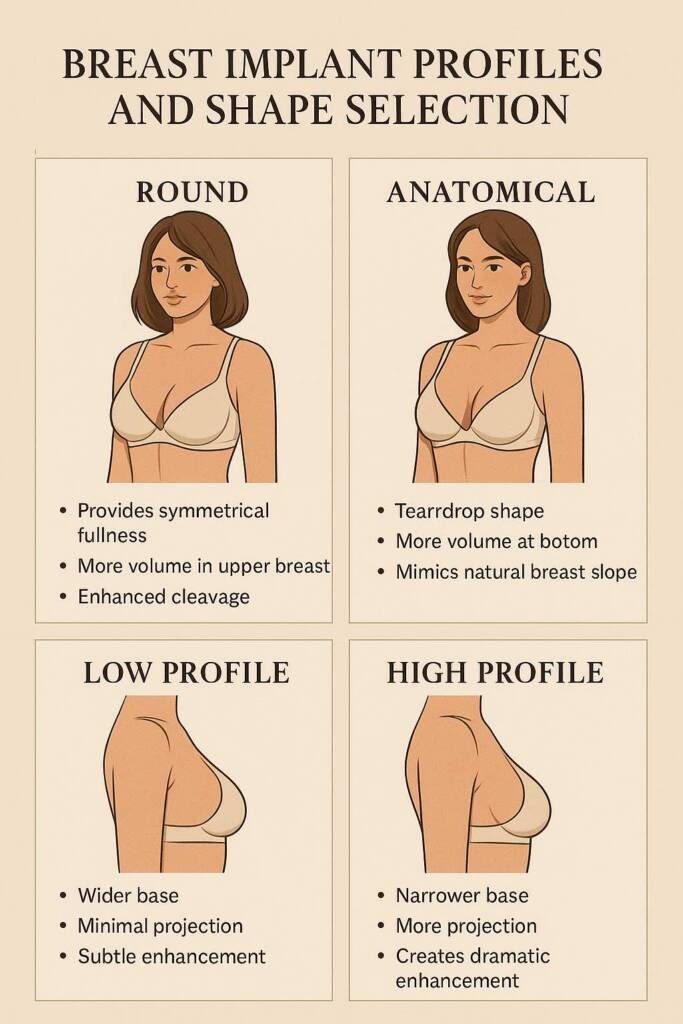
Round Versus Anatomical (Teardrop) Implants
Round implants provide symmetrical fullness throughout the entire breast area. They create more volume in the upper portion and result in enhanced cleavage and pronounced augmented appearance. These implants can rotate without affecting breast shape since they maintain the same contour from all angles.
Anatomical (teardrop) shaped implants mimic natural breast slope with more volume at the bottom and tapering toward the top. This creates gradual, natural-looking curves. However, they require textured surfaces to prevent rotation, and if displacement occurs, surgical correction may be necessary.
Choosing the Right Breast Implant Size and Profile for Desired Projection
Implant profiles determine forward projection from the chest wall, affecting overall breast shape and enhancement prominence.
Low profile implants have wider bases with minimal forward projection. They spread across broader chest areas for subtle enhancement in women with wider chest measurements.
Moderate profile implants offer balanced projection and width, providing noticeable enhancement without excessive forward projection. These versatile implants typically range from 140cc to 755cc and represent the most frequently selected option for balanced enhancement.
High and ultra-high profile implants feature narrower bases with increased forward projection. They concentrate volume in smaller areas to create dramatic breast projection and enhanced cleavage.
Profile selection depends on chest width, desired projection level, and aesthetic goals for final breast appearance.
The Consultation and Breast Augmentation Surgery Process
Achieving optimal D cup results requires comprehensive planning with a qualified plastic surgeon. They must be able to customize the procedure to your unique anatomy and goals.
Selecting a Plastic Surgery Specialist
A qualified surgeon demonstrates extensive experience with breast augmentation procedures. They understand the complexities of achieving D cup proportions while maintaining natural-looking results.
At Dr. K Miami Plastic Surgery, Dr. Bart Kachniarz brings Harvard and Johns Hopkins training to every D cup augmentation procedure. This ensures natural-looking results tailored to each patient’s unique anatomy.
Planning to Choose the Right Breast Implant Size
The planning phase involves detailed measurements and anatomical assessments. Surgeons evaluate existing breast tissue, chest width, and skin elasticity. This helps determine right implant size and placement technique.
Planning elements include:
- Current breast size and tissue quality evaluation
- Precise chest wall measurements
- Implant placement location determination
- Incision technique selection
Pre-operative imaging and 3D visualization technology may show how D cup implants will appear on your frame. Sizer implants worn during consultation provide tactile feedback about weight and projection. This helps you physically experience different volumes before making final decisions.
Surgical Approach Options
Surgeons select from three primary incision approaches, each offering distinct advantages.
Inframammary fold technique places incisions underneath the breast crease. This typically results in thin 1–2 inch scars concealed within natural breast folds.
Periareolar method creates incisions along the areola’s edge. This blends with areolar pigmentation transitions while potentially preserving milk ducts most effectively.
Transaxillary approach accesses through the armpit for no breast scarring. However, it may offer less precise implant positioning.
Placement options include positioning behind chest muscle for additional tissue coverage and gradual contours. Alternatively, placement behind breast glandular tissue offers more direct projection and potentially faster recovery.
Recovery Timeline
D cup breast augmentation requires a structured recovery process to ensure optimal healing and long-term results. Understanding the timeline helps you plan appropriately and set realistic expectations.
Immediate Recovery Phase (Weeks 1–2)
Initial recovery typically takes 1–2 weeks before returning to desk work. Patients experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort during the first week. Submuscular placement often requires longer recovery than subglandular placement due to muscle involvement.
Week 1 restrictions include:
- No lifting over 10 pounds
- Sleep elevated position
- Continuous compression garment wear
- Limited arm movement
Most patients can resume light activities and desk work by week 2. However, physical restrictions continue.
Extended Recovery Phase (Weeks 3–6)
Physical restrictions last 4–6 weeks total, with gradual activity resumption. Upper body exercises require surgical clearance before resuming. Chest-specific movements like push-ups require extended recovery periods.
Progressive activity guidelines:
- Walking encouraged immediately
- Gradual exercise progression after 6–8 weeks
- Supportive athletic wear essential for all physical activities
- Complete healing indicators typically appear between 6 weeks to 3 months
Final Results Timeline (3–6 Months)
Full healing and final results after breast augmentation become apparent after 3–6 months once swelling completely subsides and implants settle into their final position. Complete settling with minimal surgical indicators typically occurs during this timeframe. This happens as tissues fully accommodate the implants.
Patients may experience temporary emotional fluctuations during body adaptation. This represents a normal part of the psychological adjustment process during physical healing.
How Long Will Implants Last?
Most implants last 10–20 years, though some may need earlier intervention due to complications or aesthetic changes. Modern implant technology allows many patients to maintain results for 15–20 years or longer with proper monitoring.
Monitoring includes:
- Annual breast examinations
- Specialized mammography techniques using displacement views
- MRI screening for silicone implants to detect silent ruptures
- Regular follow-up appointments with plastic surgeons
Potential Complications
Capsular contracture represents the most common long-term complication, with reported 10-year incidence varying broadly (roughly 2%–20%) depending on implant characteristics and surgical technique. Specifically, Allergan’s FDA-mandated Core Study for Natrelle round silicone implants found a 10-year Kaplan–Meier rate of 18.9% for primary augmentation patients. This condition occurs when scar tissue forms around implants. It can potentially cause firmness, distortion, or discomfort.
Other potential complications include:
- Implant rupture or leakage (varies by implant type)
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation (up to 15% may experience some degree of permanent sensation change, though most are minor and severe permanent loss occurs in less than 1%)
- Infection at incision sites
- Asymmetry or implant displacement
Regular monitoring helps identify complications early. Revision surgery may be necessary to address issues or aesthetic changes over time.
How Much Do D Cup Breast Implants Cost?
According to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, breast augmentation procedures average $4,875 nationally (surgeon fees only). However, comprehensive D cup augmentations including facility fees and anesthesia may reach $9,000 depending on complexity and location.
D cup augmentations often fall in the mid to upper range due to larger implant volumes and potentially more complex surgical requirements.
Many practices offer flexible payment plans through medical financing partners. This makes procedures more accessible to qualified patients.
Making Your Decision
D cup breast augmentation offers transformative results for women seeking significant yet proportionate enhancement. Success depends on careful planning, realistic expectations, and working with experienced surgeons who understand the complexities of achieving natural-looking outcomes.
Consider bringing reference photos to consultations and research public figures who share your height and frame. This helps evaluate how different breast sizes complement similar body types. This comparative approach provides realistic expectations for how implants might appear on your specific physique.
The decision should prioritize personal satisfaction over temporary aesthetic trends, ensuring long-term contentment with your enhancement. A professional consultation for breast augmentation helps determine whether D cup augmentation aligns with your anatomy, lifestyle, and aesthetic goals.
Ready to Explore Your D Cup Transformation?
Every woman’s journey to achieving ideal D cup results is unique. At Dr. K Miami Plastic Surgery, we combine world-class surgical expertise with personalized care. We help you achieve the natural, beautiful results you deserve.
Dr. Kachniarz offers complimentary initial consultations to discuss your goals, assess your anatomy, and create a customized plan for your D cup augmentation.
source https://drkmiamiplasticsurgery.com/d-cup-breast-implants-guide-to-sizing-choices